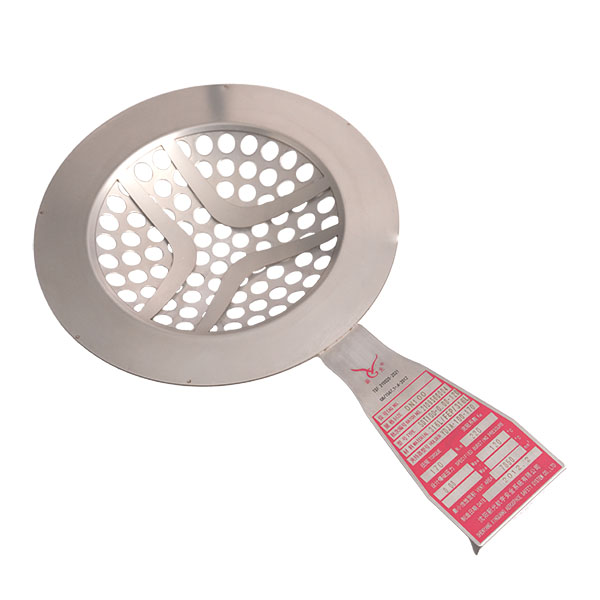
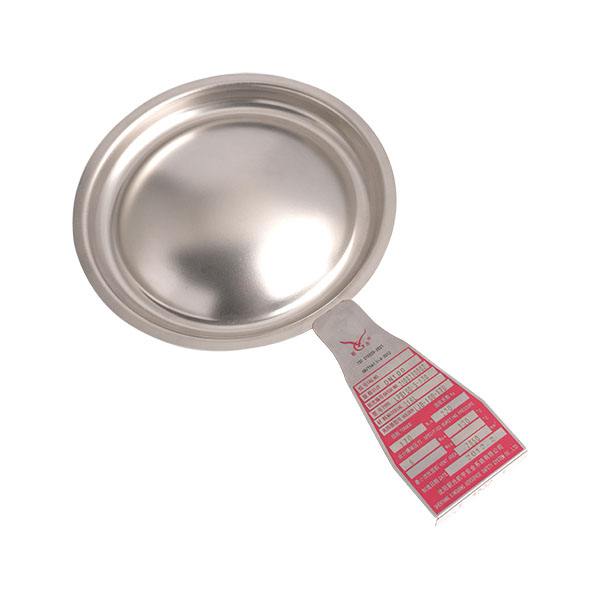
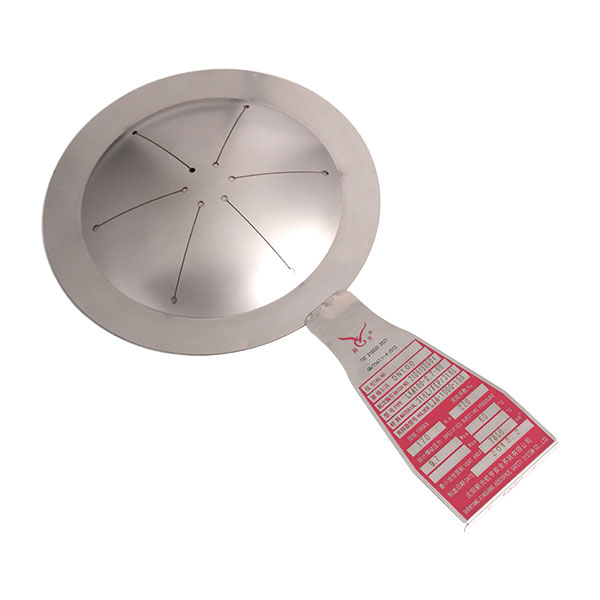
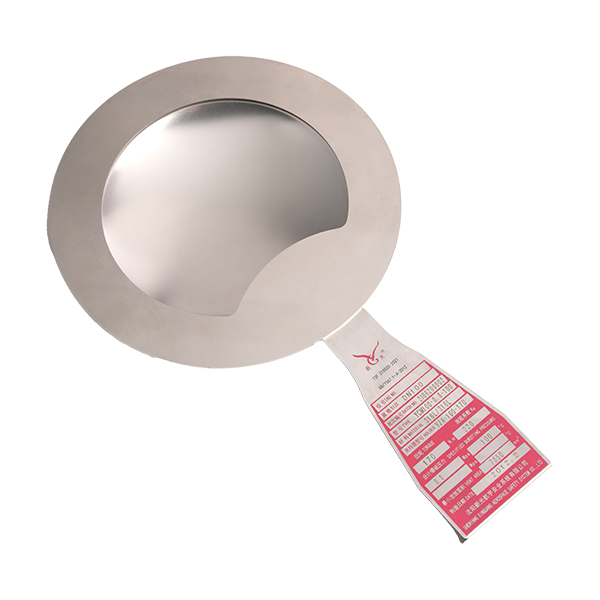
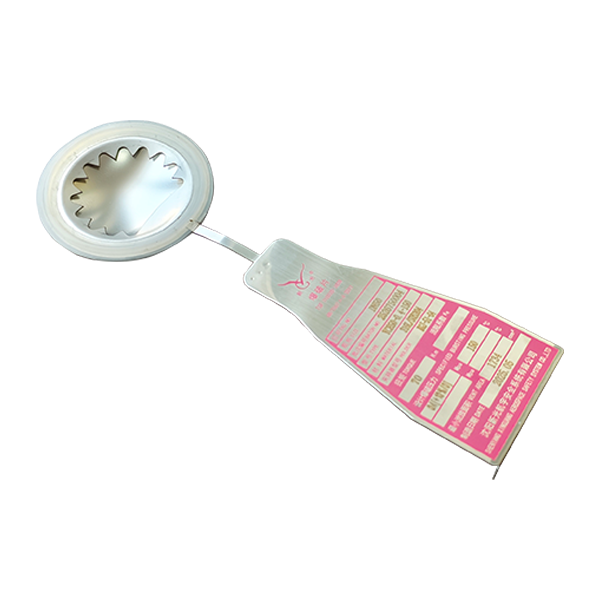
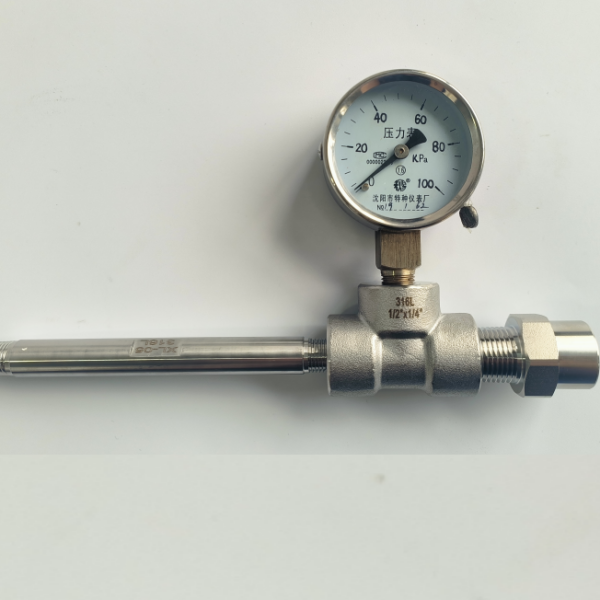
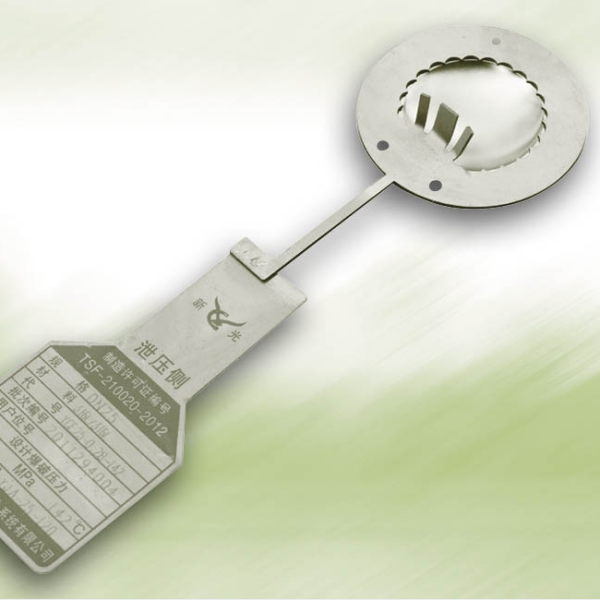
When a high temperature rupture disc ruptures, it means the internal system pressure has exceeded the predetermined safety limit, or the high-temperature rupture disc has failed due to fatigue or corrosion. This is a safety emergency and requires immediate action.
The following are the standardized procedures you should follow, divided into three stages: emergency response, troubleshooting, and recovery operations:
1. Emergency Response Stage (Immediate Action):
Upon discovering a ruptured high-temperature rupture disc (usually accompanied by a loud pressure release sound, a sudden drop in pressure gauge readings, or activation of the alarm system):
• Ensure personnel safety: If the medium is toxic, flammable, or a high-temperature fluid, immediately evacuate surrounding personnel to a safe area. Ensure operators wear appropriate personal protective equipment.
• Stop the pressure source: Immediately shut down the equipment causing the pressure increase (e.g., pumps, compressors, heaters, etc.). Close the inlet valve to prevent further pressure buildup.
• Isolate the system: If possible and safe, close the upstream and downstream isolation valves to isolate the affected equipment from the rest of the system and prevent further material leakage.
• Monitor the discharge:
If the high-temperature rupture disc is directly connected to the atmosphere, confirm that there are no personnel around the discharge port and be alert for secondary hazards (such as fire).
If the high-temperature rupture disc is in series below a safety valve, rupture may cause the safety valve to activate or simply cause pressure to build up between the two components; the status needs to be confirmed via a pressure gauge.

2. Troubleshooting and Analysis (Before Replacement):
After the system pressure has dropped to zero and safety is ensured, do not rush to immediately replace the new high-temperature rupture disc; the cause must first be determined:
• Confirm the cause of rupture:
Overpressure rupture: Check process data (DCS records) to confirm whether the system actually experienced overpressure. If overpressure did occur, the underlying process problem causing the overpressure must be resolved (e.g., temperature control failure, valve blockage, etc.).
Fatigue/Aging: If the system was not overpressurized but the high-temperature rupture disc ruptured, it may be due to fatigue caused by long-term pulsating pressure, corrosion, or improper installation (uneven torque).
Back pressure influence: Check if there is back pressure in the discharge line, causing abnormal stress on the high-temperature rupture disc.
• Check for fragments: Fragments may be produced after the high-temperature rupture disc ruptures (especially non-scored types). The downstream piping, safety valve inlet, or inside the equipment must be inspected, and all metal debris must be removed to prevent pipe blockage or damage to downstream equipment.

3. Replacement and Restoration Phase (Maintenance Operation).
• Prepare spare parts:
Verify that the specifications (burst pressure, temperature, material, and diameter) of the new high-temperature rupture disc are exactly the same as the old one and meet the process requirements.
Note: Burst pressure is usually related to temperature; ensure that the spare part is suitable for the current operating temperature.
• Inspect the holder:
Clean the sealing surface of the holder; it must be free of rust, dirt, or old gasket residue.
Check the holder for deformation or scratches. A damaged holder can lead to poor sealing of the new rupture disc or deviations in burst pressure.
• Correct installation:
Directionality: Install strictly according to the flow direction arrow on the high-temperature rupture disc. Installing it incorrectly will cause a significant increase in burst pressure (possibly several times higher), which is extremely dangerous.
Torque control: Use a torque wrench and tighten the bolts evenly in a diagonal cross pattern according to the torque value specified by the manufacturer. Excessive or insufficient torque will change the burst pressure.
• Leak test: After installation, perform an appropriate airtightness test to ensure there are no leaks.