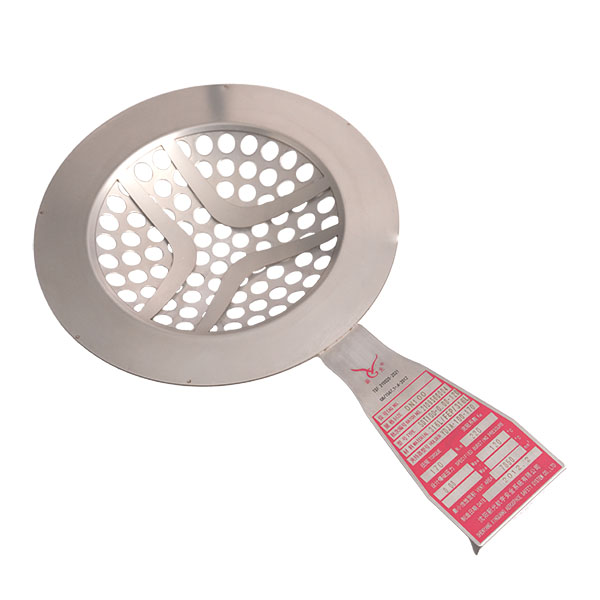
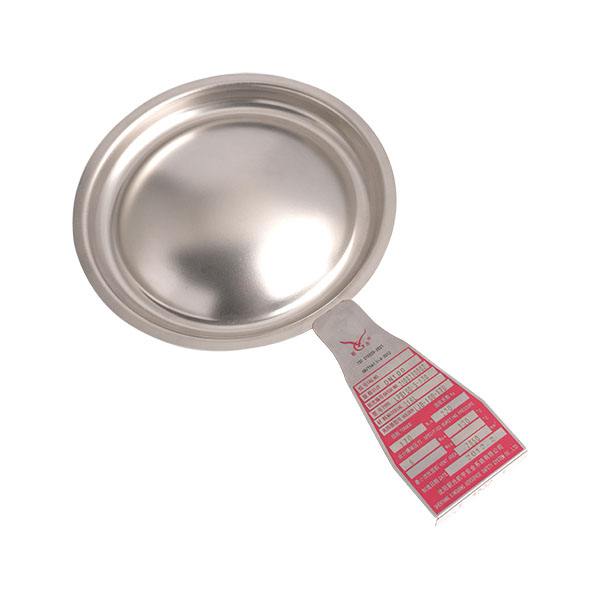
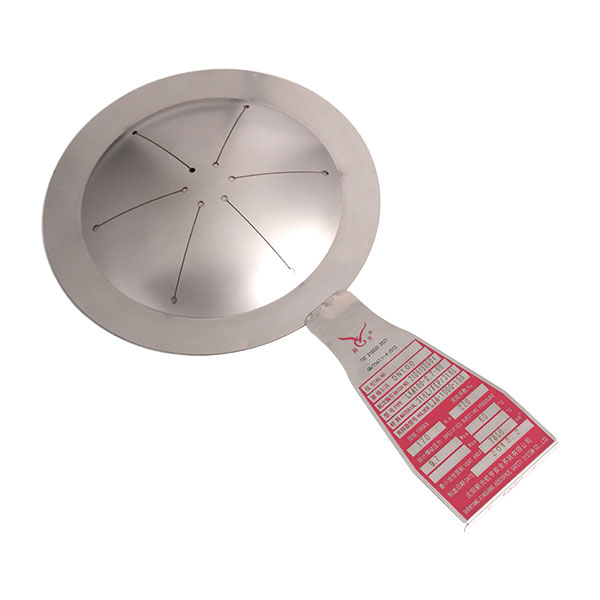
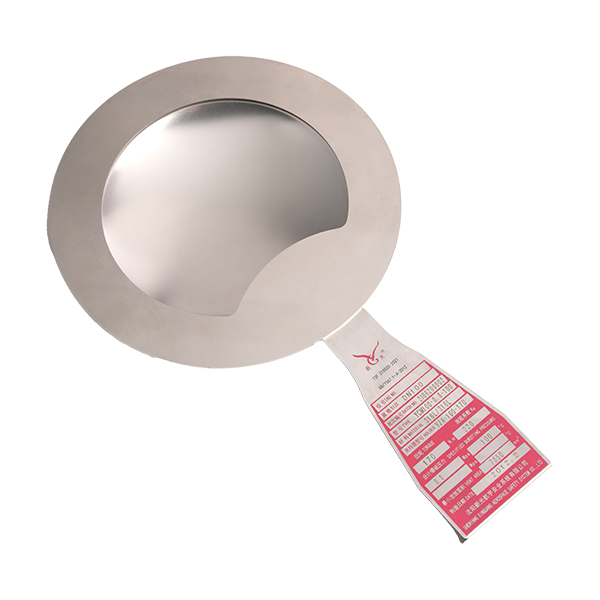
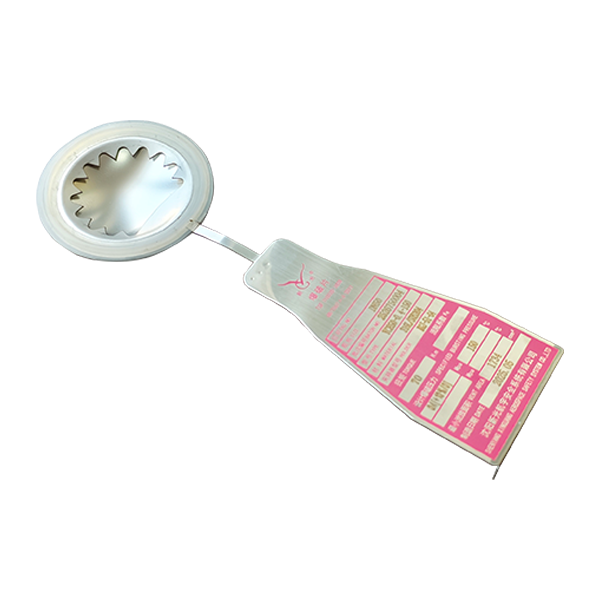
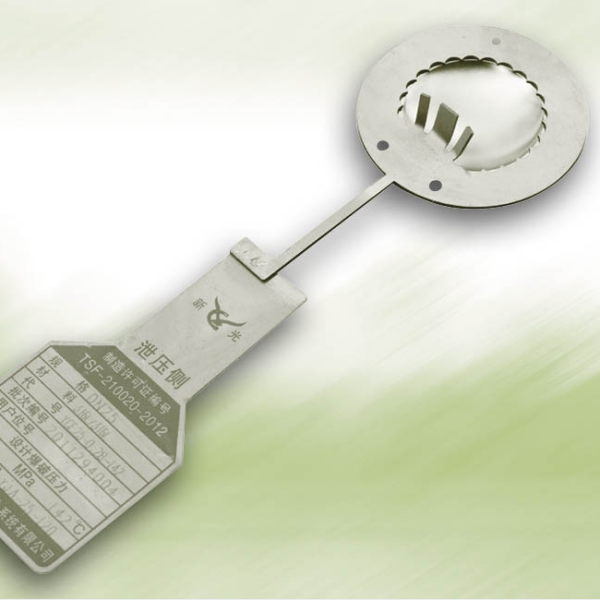
Rupture discs are pressure relief devices widely used in industries such as petrochemical, pharmaceutical, nuclear power, and defense. Their main function is to protect equipment and systems from damage caused by overpressure. Among the various designs available, thin rupture discs are typically forward-acting (positive acting), while thick rupture discs are usually reverse-acting. These two types differ significantly in structure, performance, and suitable operating conditions.
Thin rupture discs use relatively thin materials, with pressure applied to the concave side, causing the disc to fail under tensile stress. Thick rupture discs, on the other hand, use thicker materials, with pressure applied to the convex side, placing the disc under compressive stress. This structural difference directly affects their performance characteristics.
Performance Comparison:
Fatigue Resistance and Operating Ratio:
The operating ratio refers to the relationship between the system’s normal operating pressure and the disc’s burst pressure. Pressure relief rupture discs with a thin design generally have a lower operating ratio and are better suited for systems with stable pressure conditions.
Thick rupture discs use a compression-loaded design, which provides stronger fatigue resistance and allows for a higher operating ratio. They can withstand long-term operation closer to the burst pressure and are therefore more suitable for dynamic or frequently fluctuating pressure conditions.

Burst Response and Accuracy:
Thin rupture discs respond quickly to pressure changes because they rupture through material stretching. This makes Pressure relief rupture discs a good choice for applications that require rapid pressure release. Since the material is thinner, selecting corrosion-resistant alloys can help maintain burst accuracy under challenging media conditions.
Thick rupture discs rupture by reversing and opening along a knife-edge structure. Their response mechanism differs from thin discs, but they typically offer a longer service life and more stable long-term performance.
Fragmentation and Relief Characteristics:
Thin rupture discs may generate some fragments after bursting, and the pressure relief process is more direct. They are suitable for general media environments where fragment control is not critical.
Thick rupture discs are usually designed as non-fragmenting structures, producing little to no debris after activation. This makes them suitable for applications with strict requirements for media purity and downstream equipment protection, where fragment-free relief is essential.
Selection Recommendations:
When selecting a rupture disc, it is important to evaluate the full set of operating conditions, including working pressure, temperature, process media, pressure cycling frequency, and whether non-fragmenting performance is required.
Thin disc applications:Choose Pressure relief rupture discs when pressure fluctuations are minimal, fast response is required, and cost efficiency is a priority for standard operating conditions.
Thick disc applications:Thick rupture discs are preferred when pressure cycling is frequent, fatigue resistance is critical, the media is highly corrosive, or fragment-free protection is required—such as in high-pressure pulsating systems or toxic media service.
For best results, prepare detailed operating data and consult with an experienced manufacturer to ensure compliance with applicable standards and required certifications.

Shenyang Xinguang has more than 60 years of experience in the research, manufacturing, sales, and service of rupture disc safety devices, holds over 30 independent intellectual property rights, and is certified to CE and ASME UD standards.
We offer a wide range of rupture disc types with diverse material options, serving demanding industries such as petrochemical, pharmaceutical, nuclear power, and defense. With a long-standing focus on reliable safety protection and professional technical support, we welcome global procurement partners to contact us and work together toward safer and more efficient system operation.