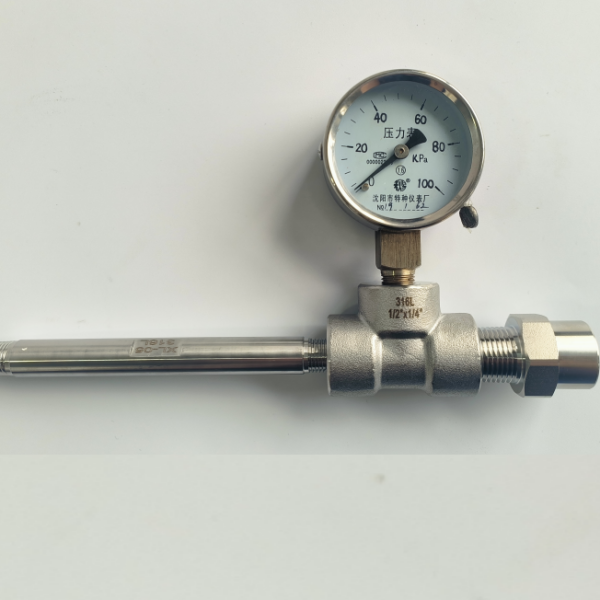
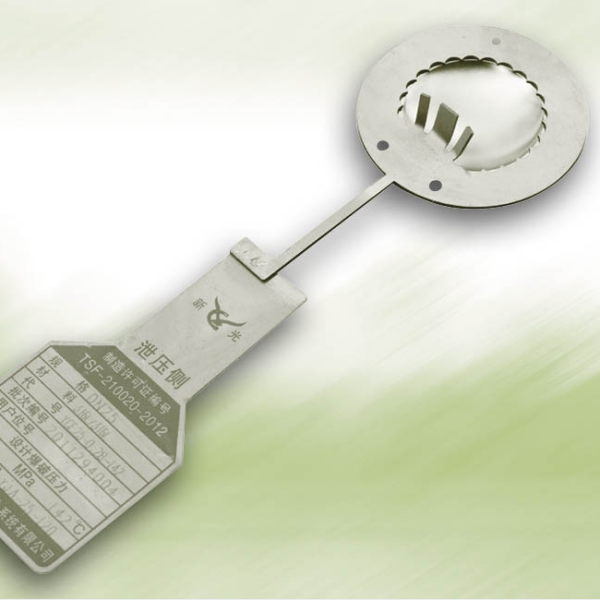
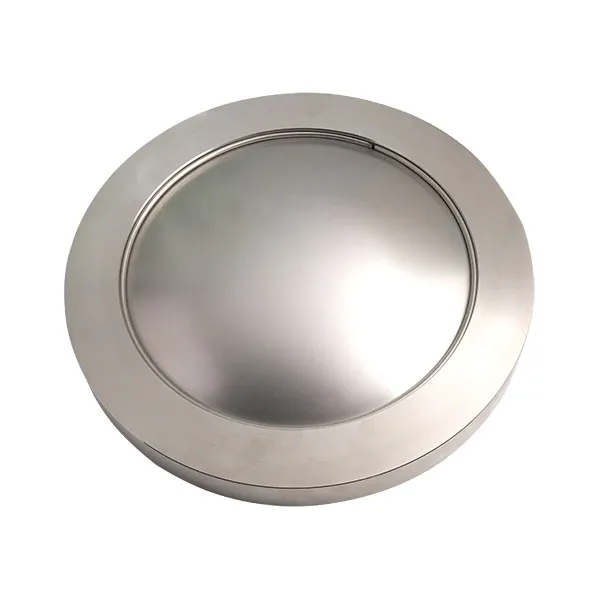
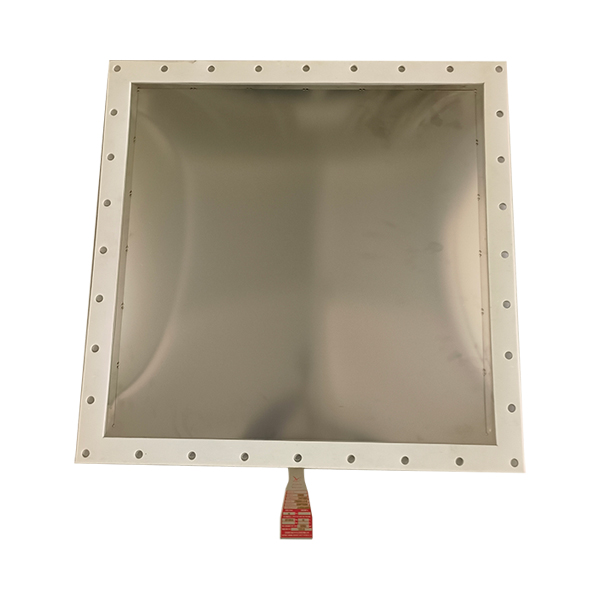
A bursting disc is a non-reclosing pressure relief device used to protect pressure vessels, pipelines or systems from overpressure damage. When the system pressure exceeds the preset value, the bursting disc ruptures instantly, releasing the pressure and ensuring the safety of the equipment.
1. Application scenarios:
- Industrial processes such as chemical, petroleum, and natural gas.
- Special fields such as nuclear power and aerospace.
- Used in series with safety valves to improve redundant protection.
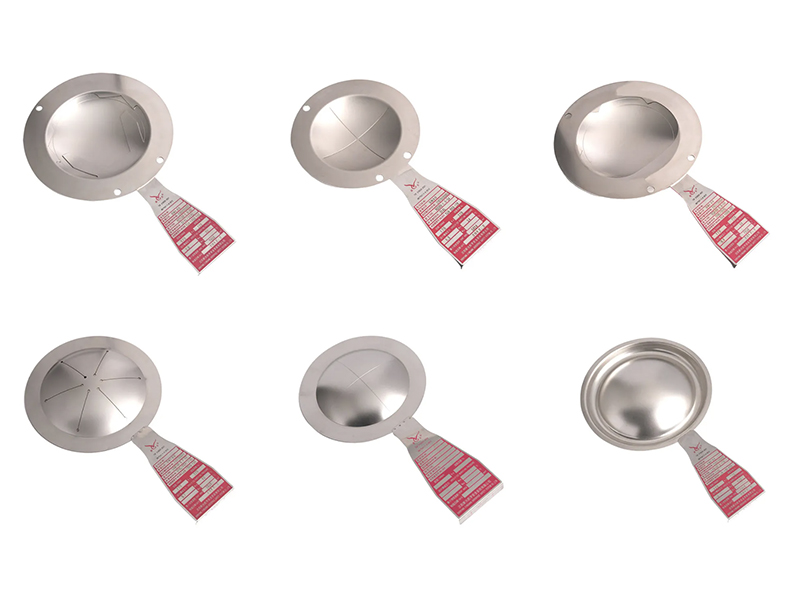

2. Core parameters for selection of bursting discs:
Pressure parameters:
Design bursting pressure (MAWP): The bursting pressure value calibrated by the bursting disc must be determined in combination with the system maximum allowable working pressure (MAWP) and safety factor.
Operating pressure range: The normal working pressure of the system should be lower than 90% of the minimum bursting pressure of the bursting disc.
Back pressure effect: If there is back pressure (such as in series with a safety valve), a back pressure resistant bursting disc (such as an inverted arch) must be selected.
Medium characteristics:
Medium type: gas, liquid or gas-liquid two-phase flow.
Corrosion: Choose corrosion-resistant materials (such as Hastelloy, nickel, graphite, etc.) according to the chemical properties of the medium.
Solid particles or sticky substances: Preferentially use flat-type bursting discs with protective coatings to avoid clogging.
Temperature conditions:
Operating temperature range: The temperature resistance of different materials (such as stainless steel, tantalum, polytetrafluoroethylene) varies significantly.
Temperature fluctuations: Frequent thermal cycles may affect the fatigue life of the bursting disc, and anti-fatigue design needs to be selected.
| Type | Features | Applicable scenarios |
| Positive arch | Affected by compression force, sensitive to pressure fluctuations | Pure gas, low pressure scenarios |
| Reverse arch | Affected by tensile force, strong fatigue resistance, can withstand back pressure | High pressure, corrosive media or particle-containing scenarios |
| Flat plate | Simple structure, corrosion resistance, but low pressure bearing capacity | Low pressure, high purity media |
| Graphite type | High temperature resistance, corrosion resistance, brittle materials | Strong acid, strong alkali or ultra-high temperature environment |
Technical Guide for Selection of Bursting Discs (2) will be updated tomorrow. New and old customers are welcome to consult us at any time. Wish you all the best today.