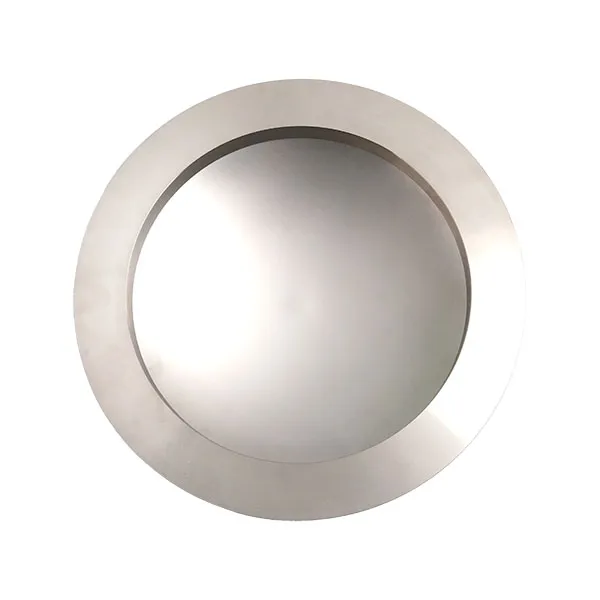
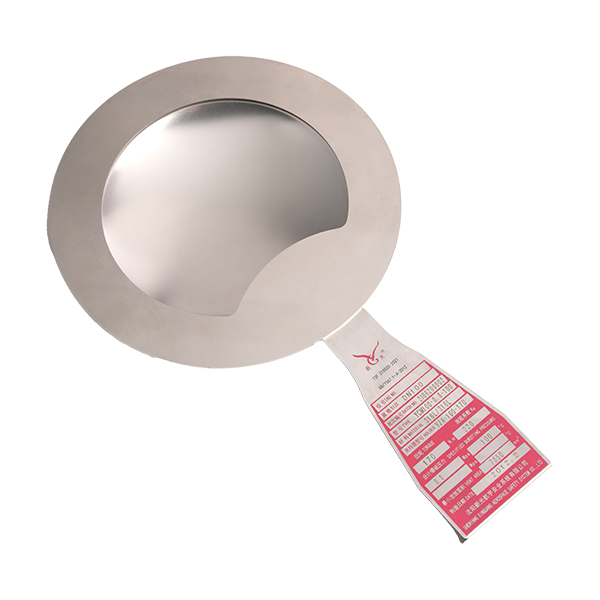
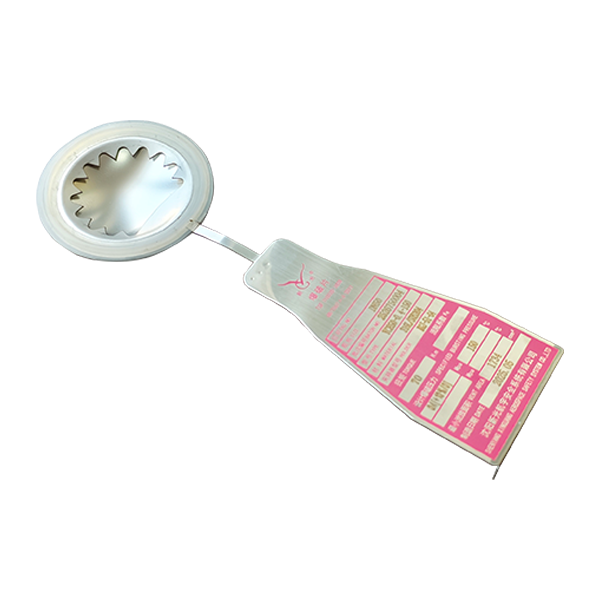
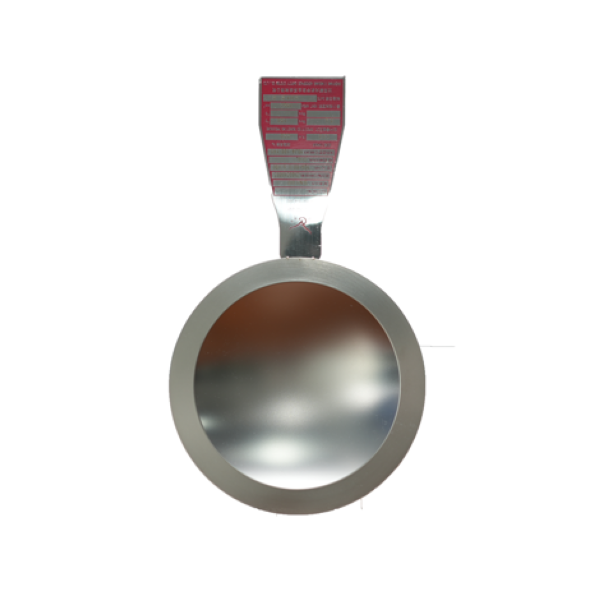
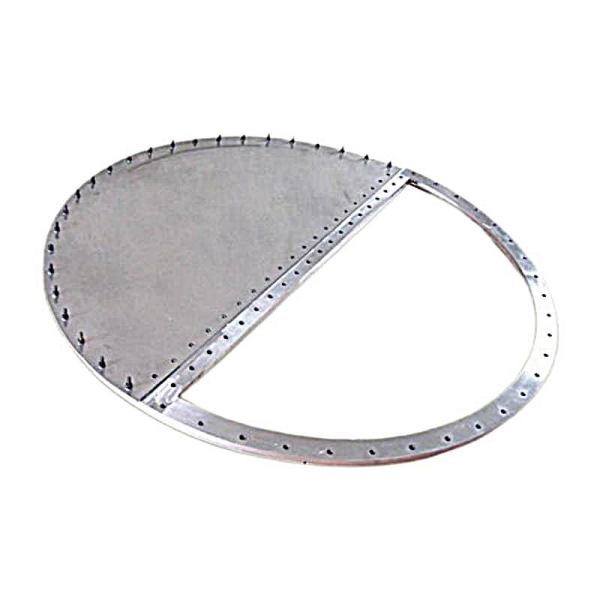
As an important safety device for industrial pressure equipment, LF bursting disc is known for its stable performance, but in practical applications, various problems may still occur due to factors such as installation technology, working conditions, and maintenance management. If these problems are not resolved in time, they will not only reduce the effect of safety protection, but may even cause the risk of equipment overpressure. Therefore, understanding the common problems and solutions of LF bursting disc is very important for the operation of the blasting disc.
The deviation of burst pressure beyond the design range is the most common problem in the use of LF bursting disc. During the operation of the equipment, some enterprises found that the deviation between the actual burst pressure of the LF bursting disc and the set value exceeds the standard requirement of ±5%, which leads to unnecessary early blasting and loss of downtime. In the heavy case, the overpressure did not act in time, causing a safety accident. The reasons for this problem include improper material selection, insufficient machining accuracy and installation stress. When the temperature of the medium far exceeds the design value, the mechanical properties of the metal material will change, resulting in a decrease in the burst pressure. However, if the flange bolts are not tightened evenly during installation, the positive arch structure will produce additional stress and change the original pressure bearing characteristics. To solve this problem, it is necessary to strictly follow the principle of material adaptation, select the corresponding grade of material according to the temperature and pressure parameters, and use a torque wrench to fasten the bolts in a symmetrical order to make the installation stress uniform.
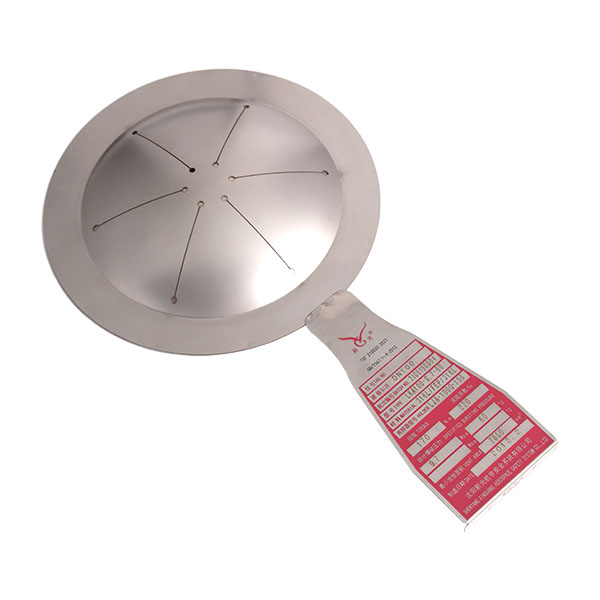

LF bursting disc is prone to corrosion failure in corrosive environments, which is manifested as pitting, cracks or thickness thinning on the surface of LF bursting disc, which eventually leads to abnormal burst pressure or seal failure. This problem is particularly prominent in the treatment of strong acids, alkalis or chloride-containing ionic media. If ordinary stainless steel is used without anticorrosive treatment, corrosion damage may occur in just a few months. To deal with corrosion problems, we need to start from both material upgrading and process optimization. It is best to give priority to corrosion-resistant materials such as hastelloy and titanium alloys, or to perform surface treatments such as PTFE coating and electroplating on LF bursting disc. At the same time, check the composition of the medium before installation to avoid chemical reactions with the material of the rupture disc, regularly check the surface corrosion condition through the endoscope, and replace the aging parts in time.
In the operating conditions of frequent pressure fluctuations or alternating high and low temperatures, the LF bursting disc may have extreme problems of malfunction or non-operation of overpressure. The malfunction is mostly caused by the water hammer effect and medium impact during the start-up and stop of the equipment, especially when the centrifugal pump starts suddenly, the instantaneous pressure peak in the pipeline may trigger the LF bursting disc to break early. Inaction is often related to blockage of notches and material fatigue. When impurities in the medium are deposited at the slotted site, it will hinder the rupture path and cause normal discharge during overpressure. To solve such problems, the system design needs to be optimized, a buffer device is installed upstream of the rupture disc to reduce the pressure impact, and a filter is added to prevent impurities from clogging. For long-term operating equipment, the burst pressure review test can also be carried out in accordance with the prescribed cycle to avoid performance degradation caused by material fatigue, and at the same time, the pressure buffer interval is set in the control program to reduce the impact of frequent fluctuations on the LF bursting disc.